Grade 9 exploring interior angles of polygons filetype pdf
Adjacent angles have a common vertex and a common arm, e.g. 1 and 2,ˆ ˆ ˆˆ2 and 3, 3 and 4ˆ ˆ or 1 and 4.ˆˆ Vertically opposite angles lie opposite each other,
The sum of the measures ofa the interior angles ofa n n-gon is… A polygon that is both equilateral and equiangular. The measure of aeach interior angle ofa regular n-gon is ((n-2…
(interior) angles of the polygons that meet at each point do not add up to 360°. b. You could use trapezia, rhombuses, or triangles with hexagons to make a tessellation. For example: trapezia and hexagons rhombuses and hexagons triangles and hexagons 3. A tessellation with triangles and squares could look like this: 4. Side lengths that meet must be the same and the interior angles of the
Grade 10- Geometry Module •Congruence, Proof Students visualize, with the aid of appropriate software tools, changes to a three-dimensional model by exploring the consequences of varying parameters in the model . Alignment Chart Module and Approximate Number of Instructional Days Common Core Learning Standards Addressed in Geometry Modules Module 1: Congruence, Proof, …
ANGLES: POLYGONS Materials required for examination Items included with question papers Ruler graduated in centimetres and Nil The size of each interior angle of a regular polygon is 156°. Work out the number of sides of the polygon… (3 marks) 6. Here is a regular polygon with 9 sides. Diagram NOT accurately drawn Work out the size of an exterior angle
Interior Angles in Polygons UNIT 15 Polygons Lesson Plan 2 Verbal checking of all homework exercises. Each figure appears on OHP (one at a time) and a volunteer P repeats the fact they have reviewed in the previous lesson and gives the solution. Other Ps agree/correct; T praises. Feedback, self-correction. Praising. (continued) Whole class activity. Ps have stated the facts about the angles …
(9. th. grade) 1. The measure of a regular polygon’s interior angle is four times bigger than the measure of its external angle. How many sides does the polygon have? Solution to Problem 1 . 2. How many sides does a convex polygon have if all its external angles are obtuse? Solution to Problem 2 . 3. Show that in a convex quadrilateral the bisector of two consecutive angles forms an angle
Math Handbook of Formulas, Processes and Tricks 26 Polygons – More Definitions (Definitions, Diagonals of a Polygon) 27 Interior and Exterior Angles of a Polygon Geometry Handbook Table of Contents Cover art by Rebecca Williams, Twitter handle: @jolteonkitty Version 3.2 Page 2 of 82 August 28, 2018. Geometry Handbook Table of Contents Page Description Chapter 6: Quadrilaterals 28
find and use the measures of interior and exterior angles of polygons.” I. Definitions A 9) Draw the following, or tell why it cannot be drawn. A. Concave equilateral pentagon B. Concave trapezoid C. Irregular Equilateral triangle D. Convex irregular heptagon 10) Tell whether each statement is Always, Sometimes, or Never true. A. An equiangular triangle is a regular convex polygon B. A
EXPLORING TESSELLATIONS Background: What is a tessellation? A tessellation is any pattern made of repeating shapes that covers a surface completely without overlapping or leaving any gaps. A checkerboard is a tessellation made of squares. The squares meet edge to edge with no gaps and no overlapping areas. The pattern of bricks on a wall is a tessellation made of rectangles. Over 2,200 …
and angles. Polygons can be sorted into families according to the number and lengths of their sides and the measures of their angles. • Patterns exist among interior and exterior angles in polygons. For example, the sum of the interior angles of a polygon relates to the number of triangles that are formed by drawing diagonals from one vertex. Relationships Among Angles: Understand special
Gr 9 Maths Content Area 3 & 4 Geometry & Measurement (2D)

The Point in Polygon Problem for Arbitrary Polygons
6 1 practice the polygon pdf15 polygons mep y8 practice book b – cimt.org.ukpractice papers set 1 – higher tier (pdf, 1mb) – ocr.org.ukthe measures of the interior angles in a polygon arejmap by topic
polygon, describe the rotations and reflections that carry it onto itself. [G.CO.3] CB 9-3 : 4. Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. [G.CO.4] 9-1, 9-2, 9-3 . 5. Given a geometric figure and a rotation, reflection, or translation, draw the transformed figure using, e.g., graph paper
Remember that if two polygons are similar, then both polygons have the same interior angles, but not necessarily the same side lengths. If similar polygons also have the …
400 Chapter 10 Polygons and Area CHAPTER1010 Polygons and Area > Make this Foldable to help you organize information about the material in this chapter.
Geometry (H) Lesson 6.1 6. Find the sum of the measures of the exterior angles of the given regular polygon. You will be responsible for reporting your results to the class.
and relationships of the interior and exterior angles of triangles, quadrilaterals, and other polygons, and apply the results to problems involving the angles of polygons; ¾ Determine, through investigation using a variety of tools, and describe the properties and relationships of the angles formed by parallel lines cut by a transversal, and apply the results to problems involving parallel
Applied Math Area of Polygons Chapter 12 . Area of Polygons. 12.1 Polygon bounded by a number of straight lines is called polygon. A polygon is said to be regular when all its sides and angles are equal. A five sided polygon is called a pentagon. A six sided polygon is called a hexagon.
The interior angles of the triangle, square and hexagon are 60, 90, and 120, respectively which works. There does not exist any other regular polygon with this property. 6 Lesson Overview 1. The aim is to get students working together in groups using a discovery method for students to learn the ideas of polygons angles and construction using the Zome System. For students who are new to the
Standard G.9 The student will use measures of interior and exterior angles of polygons to solve problems… Lesson 8-1 Angles of Polygons 405 Interior Angles of Regular Polygons
INTERIOR ANGLE SUM THEOREM: The sum of the measures of the interior angles of any polygon with n sides is (n-2) x 180o. _____ In order to prove this theorem, we first prove something quite similar, but different. Namely, that any polygon with n vertices (a polygon with n vertices of course has n sides) can be divided into a collection of n-2 triangles which, when put together, fill the entire

a convex region [interior] and a non-convex region [exterior] of the plane.) -Paper can be folded so that straight lines on the same sheet can be made coincident. -Line and angles are said to be congruent when they can be made to coincide by
MATHEMATICS 1.9 – AS90153 Geometric reasoning Santa lives here Running round in circles Circle border Bottom of circle Inside Circle Intruding square
But the sum of the interior angles is (n – 2) × 180°, so the sum of the exterior angles is always 2 × 180° = 360°. Find, calculate and use the interior and exterior angles of a regular polygon with n sides. For example: • The interior angle sum S for a polygon with n sides is S = (n – 2) × 180°. In a regular polygon all the angles are equal, so each interior angle equals S divided
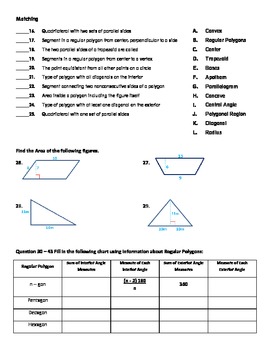
Grade 8: Chapter 5, Lesson 4: pgs. 397-404 Polygons and Angles Part 1: Interior Angle Sum of a Polygon The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon is , where represents the number of sides. You can use the sum of the angle measures of a triangle to find the sum of the interior angle measures of various polygons. A polygon that is equilateral (all sides are the same length) …
Arbitrary convex polygons 144 §9. Pascal’s theorem 145 Problems for independent study 145 Solutions 146 Chapter 7. LOCI 169 Background 169 Introductory problems 169 §1. The locus is a line or a segment of a line 169 * * * 170 §2. The locus is a circle or an arc of a circle 170 * * * 170 §3. The inscribed angle 171 §4. Auxiliary equal triangles 171 §5. The homothety 171 §6. A method of
Polygons and Angles Date_____ Period____ Find the measure of one interior angle in each polygon. Round your answer to the nearest tenth if necessary.
INTERIOR ANGLE SUM THRMed Office of Technology Services
Improve your math knowledge with free questions in “Interior angles of polygons” and thousands of other math skills.
Postulate 9: If a point D lies in the interior of angle ABC, then m ABD + m DBC = m ABC Theorem 1.4.1: There is one and only one angle bisector for any given angle.
Theorems include: measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180°; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a – same material interior and exterior pdf 9. What polygon has 6 sides and 6 angles? _____ 10. Name four types of quadrilaterals. Polygons 1. How many sides does an octagon have? eight 2. How many angles does a triangle have? three 3. Does a rectangle have more sides or angles? same number (four) 4. How many sides does a pentagon have? five 5. Which has more sides: a hexagon or a pentagon? hexagon 6. How many pairs of parallel
the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 ,∞ it follows that the sum of the measures of the interior angles of an n -sided polygon is ()() n -∞2 180 .
sums of interior angles of polygons. LESSON3 Angles in Heptagons 9 Date Time 1. A heptagon is a polygon with 7 sides. Predict the sum of the angles in a heptagon. 2. Draw a heptagon below. Measure its angles with a protractor. Write each measure in the angle. Find the sum. Sum of the angles in a heptagon 3. a. Is your measurement close to your prediction? b. Why might your prediction and
polygon veritcal line curve triangle arc scalene triangle rhombus diagonal line right angle square octagon ellipse isosceles triangle trapezoid parallel lines acute angle rectangle polygon right triangle quadrilateral tesselation cylinder tetrahedron sphere rectangular prism octahedron cone Solid Figures Geometry Scavenger Hunt. Created Date: 9/22/2010 8:45:20 PM
only be reduced for special polygons, e.g. if the polygon is convex, an O(logn) algorithm can be found [7, 8, 10]. The performance of the different algorithms is
3 Angles in Polygons Fill in the accompanying table. Polygon Number of Sides Number of Triangles Sum of Interior Angle Measures 3 1 180
6 1 Practice The Polygon Angle Sum Theorems Form K
Measuring Angles sheet Math Worksheets 4 Kids
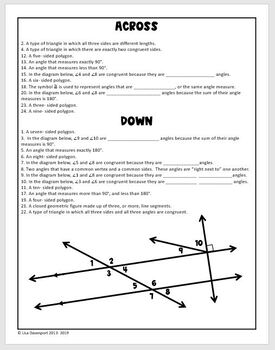
Y8 UNIT 15 Polygons Lesson Plan 1 Angles CIMT
Triangles WordPress.com



–
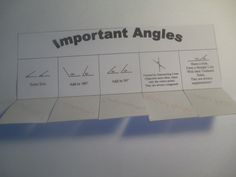

Y8 UNIT 15 Polygons Lesson Plan 1 Angles CIMT
Part 1 Interior Angle Sum of a Polygon represents the
(interior) angles of the polygons that meet at each point do not add up to 360°. b. You could use trapezia, rhombuses, or triangles with hexagons to make a tessellation. For example: trapezia and hexagons rhombuses and hexagons triangles and hexagons 3. A tessellation with triangles and squares could look like this: 4. Side lengths that meet must be the same and the interior angles of the
Theorems include: measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180°; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a
3 Angles in Polygons Fill in the accompanying table. Polygon Number of Sides Number of Triangles Sum of Interior Angle Measures 3 1 180
find and use the measures of interior and exterior angles of polygons.” I. Definitions A 9) Draw the following, or tell why it cannot be drawn. A. Concave equilateral pentagon B. Concave trapezoid C. Irregular Equilateral triangle D. Convex irregular heptagon 10) Tell whether each statement is Always, Sometimes, or Never true. A. An equiangular triangle is a regular convex polygon B. A
only be reduced for special polygons, e.g. if the polygon is convex, an O(logn) algorithm can be found [7, 8, 10]. The performance of the different algorithms is
Geometry (H) Lesson 6.1 6. Find the sum of the measures of the exterior angles of the given regular polygon. You will be responsible for reporting your results to the class.